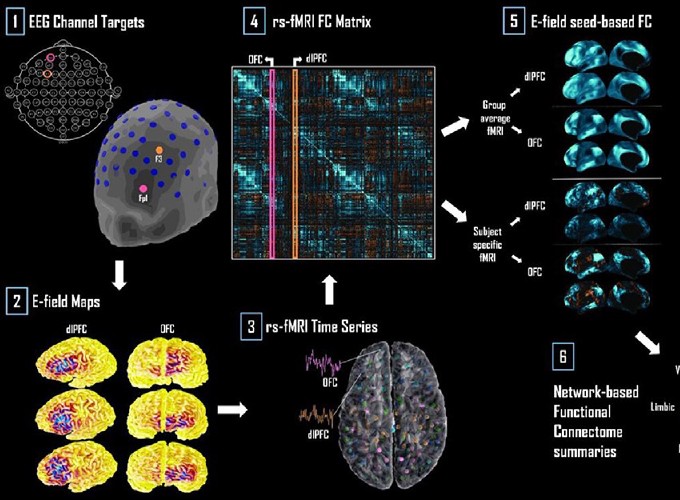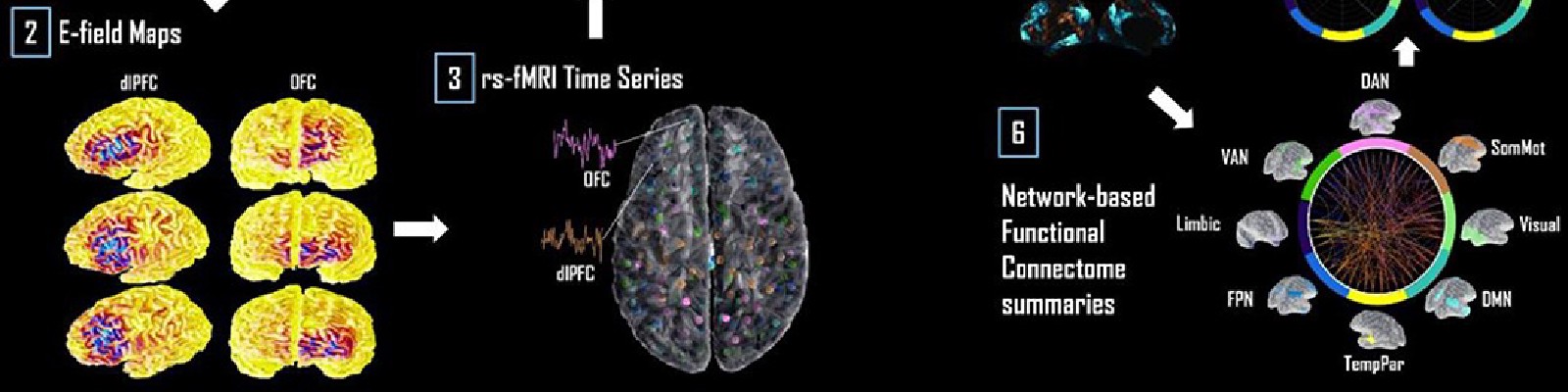
Mapping inter-individual functional connectivity variability in TMS targets for major depressive disorder
Abstract
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is an emerging alternative to existing treatments for major depressive disorder (MDD). The effects of TMS on both brain physiology and therapeutic outcomes are known to be highly variable from subject to subject, however. Proposed reasons for this variability include individual differences in neurophysiology, in cortical geometry, and in brain connectivity. Standard approaches to TMS target site definition tend to focus on coordinates or landmarks within the individual brain regions implicated in MDD, such as the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) and orbitofrontal cortex (OFC). Additionally considering the network connectivity of these sites (i.e., the wider set of brain regions that may be mono- or poly-synaptically activated by TMS stimulation) has the potential to improve subject-specificity of TMS targeting and, in turn, improve treatment outcomes. In this study, we looked at the functional connectivity (FC) of dlPFC and OFC TMS targets, based on induced electrical field (E-field) maps, estimated using the SimNIBS library. We hypothesized that individual differences in spontaneous functional brain dynamics would contribute more to downstream network engagement than individual differences in cortical geometry (i.e., E-field variability). We generated individualized E-field maps on the cortical surface for 121 subjects (67 female) from the Human Connectome Project database using tetrahedral head models generated from T1- and T2-weighted MR images. F3 and Fp1 electrode positions were used to target the left dlPFC and left OFC, respectively. We analyzed inter-subject variability in the shape and location of these TMS target E-field patterns, their FC, and the major functional networks to which they belong. Our results revealed the key differences in TMS target FC between the dlPFC and OFC, and also how this connectivity varies across subjects. Three major functional networks were targeted across the dlPFC and OFC: the ventral attention, fronto-parietal and default-mode networks in the dlPFC, and the fronto-parietal and default mode networks in the OFC. Inter-subject variability in cortical geometry and in FC was high. Our analyses showed that the use of normative neuroimaging reference data (group-average or representative FC and subject E-field) allows prediction of which networks are targeted, but fails to accurately quantify the relative loading of TMS targeting on each of the principal networks. Our results characterize the FC patterns of canonical therapeutic TMS targets, and the key dimensions of their variability across subjects. The high inter-individual variability in cortical geometry and FC, leading to high variability in distributions of targeted brain networks, may account for the high levels of variability in physiological and therapeutic TMS outcomes. These insights should, we hope, prove useful as part of the broader effort by the psychiatry, neurology, and neuroimaging communities to help improve and refine TMS therapy, through a better understanding of the technology and its neurophysiological effects.