Deep-learning based parameter estimation for neurophysiological models of neuroimaging data
Abstract
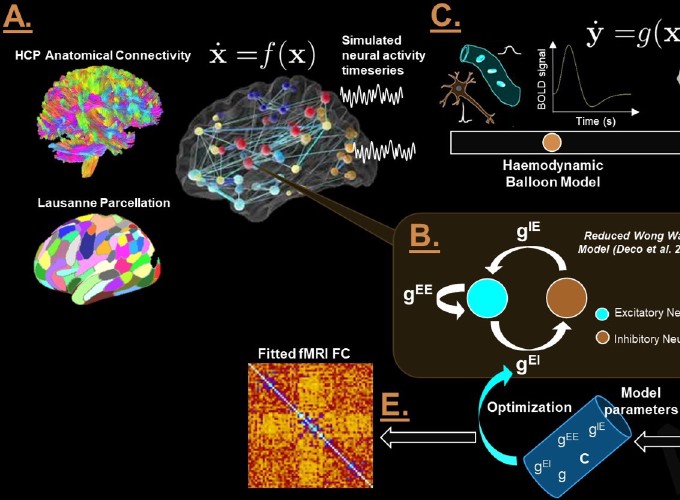
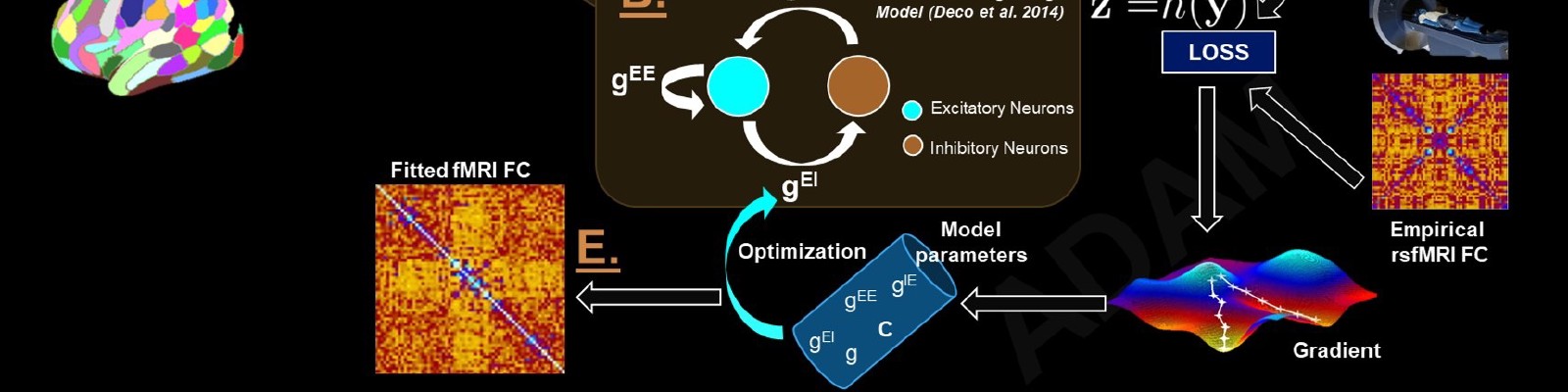
Connectome-based neural mass modelling is the emerging computational neuroscience paradigm for simulating large-scale network dynamics observed in whole-brain activity measurements such as fMRI, M/EEG, and related techniques. Estimating physiological parameters by fitting these models to empirical data is challenging however, due to large network sizes, often physiologically detailed fast-timescale system equations, and the need for long (e.g. tens of minutes) simulation runs. Here we introduce a novel approach to connectome-based neural mass model parameter estimation by employing optimization tools developed for deep learning. We cast the system of differential equations representing both neural and haemodynamic activity dynamics as a deep neural network, implemented within a widely used machine learning programming environment (PyTorch). This allows us to use robust industry-standard optimization algorithms, automatic differentiation for computation of gradients, and other useful functionality. The approach is demonstrated using a connectome-based network with nodal dynamics specified by the two-state RWW mean-field neural mass model equations, which we use here as a model of fMRI-measured activity and correlation fluctuations. Additional optimization constraints are explored and prove fruitful, including restricting the model to domains of parameter space near a bifurcation point that yield metastable dynamics. Using these techniques, we first show robust recovery of physiological model parameters in synthetic data and then, as a proof-of-principle, apply the framework to modelling of empirical resting-state fMRI data from the Human Connectome Project database. For resting state activity, the system can be understood as a deep net that receives uncorrelated noise on its input layer, which is transformed into network-wide modelled functional connectivity on its output layer. This is consistent with the prevailing conception in theoretical neuroscience of resting-state functional connectivity patterns as an emergent phenomenon that is driven by (effectively) random activity fluctuations, which are then in turn spatiotemporally filtered by anatomical connectivity and local neural dynamics.